A Project Management Office (PMO) standardizes project intake and execution, enabling organizations to concentrate on high-value initiatives and laying the foundation for successful project delivery.
These initiatives can include CRM, ERP, and cybersecurity.

What Can a PMO Do for You?
A PMO serves as a service provider, giving stakeholders confidence and assurance in their project control.
Capability Building – Enhance and develop your team’s project management skills.
Consistency – Establish and maintain consistent processes and methodologies, while providing a framework for organizational change management to ensure long-term project adoption.
Visibility – Improve transparency, alignment, and reporting on project status.
Budget and Schedule Compliance – Prevent projects from exceeding budgets, missing deadlines, or failing to meet scope and quality standards.
Accountability and Ownership – Strengthen accountability and ownership within project teams.
Communication Across Projects – Facilitate better communication and coordination across multiple projects.
Risk Management – Minimize disruptions from poorly planned project launches.
What Does the Project Management Office Do?
While there is no universally accepted list of a PMO’s functions, here are some typical responsibilities:
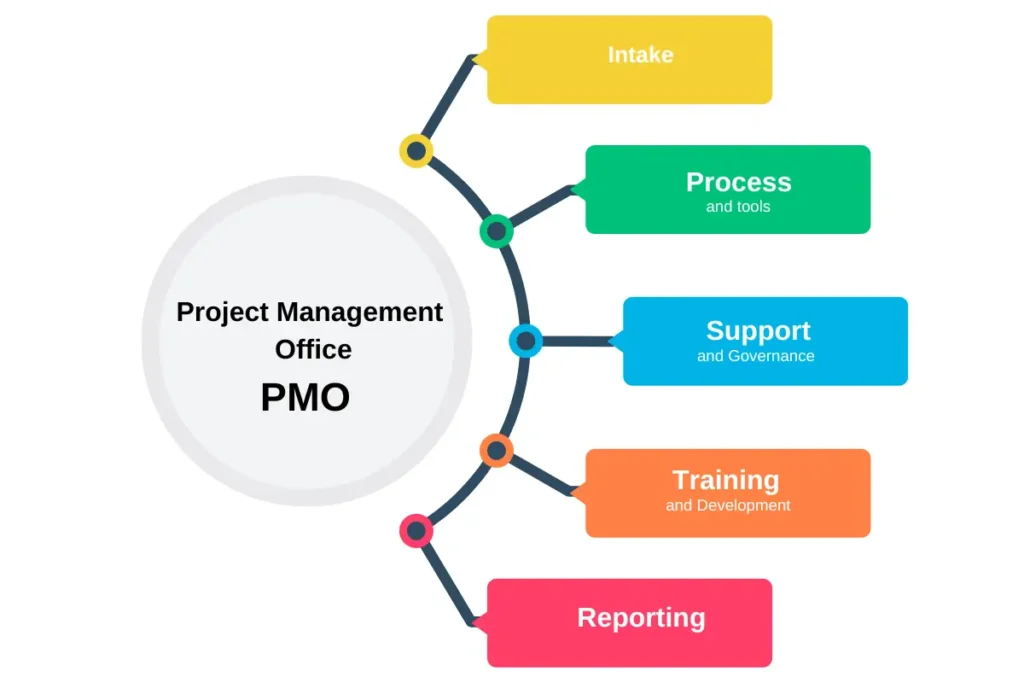
Project Intake
The PMO oversees the pipeline of new projects, handling documentation, qualification, approval, and initiation. This ensures each project is well-defined and ready for successful execution.
Managing Project Portfolio
Maintain a comprehensive overview of all projects, ensuring data and statuses are up to date. Key responsibilities include:
- Preparing project portfolio updates and reports
- Conducting portfolio meetings
- Identifying risks and implementing countermeasures
- Facilitating information flow during escalations
Develop and Promote Standards and Best Practices
Act as the steward of project management standards, ensuring they are effectively communicated and implemented organization-wide. By defining and enforcing these standards, the PMO brings consistency and stability to project management practices.
Establish Methods, Processes, and Tools
Responsible for selecting, implementing, and managing the best-fit project and portfolio management tools. The PMO encourages continuous improvement and the adoption of new technologies and practices.
- Defining and specifying processes
- Creating a project management guide
- Selecting and operating appropriate project management tools
Project Support and Governance
Provide support for project execution, including:
- Delivering planning and operational support during project implementation
- Facilitating and leading project meetings
- Offering temporary support and assistance as needed
- Providing training and mentoring to project managers, promoting best practices, and offering expert guidance and resources
Skill Development
Focus on training and upskilling project management professionals. This includes recruiting, training, and developing project management staff across various roles, such as:
- Program managers
- Project managers
- Business Systems Analysts
- Solution Architects
- Senior project coordinators/analysts
Collaboratively Define KPIs & Measure Performance
Work collaboratively with stakeholders to define project and operational metrics and KPIs. Developing these metrics in concert with business units can help avoid resistance and non-compliance.
A PMO can be an indispensable resource for any organization seeking to enhance its project management capabilities.
It addresses critical needs and challenges by providing essential skills, ensuring consistency, building capacity, and improving visibility.
It standardizes methodologies, collaborates on KPIs, focuses on skill development, and fosters continuous improvement.
To get started, a virtual PMO service can be an effective way to establish and scale these essential functions without the need for a whole in-house team.



