The ability to visualize prospect and customer address information along with firmographics and revenue data can be an important CRM adoption factor for salespeople.
For example, when a salesperson is planning a trip to a part of their territory, they can benefit from being able to visualize the highest revenue accounts within an area.
Trip planning is the classic use case for CRM data mapping, but new use cases continue to evolve with the convergence of mobile, GPS, CRM, and mapping software vendor growth.
Other Example Use Cases For Mapping Software
Sales managers can use CRM mapping software to ensure sales territories are getting proper coverage.
Marketers can review the number of CRM leads and contacts within different radii of an upcoming event. Invitations can be sent out to those within a specific radius.
Service departments can track the location of field assets and assign the appropriate support technician, taking into account proximity.
Four Levels of CRM Mapping Functionality
There are four general levels of CRM mapping software functionality available to organizations.
1. Visualize the location of an individual Lead, Contact, or Account within a CRM system
2. View multiple locations on a map by manually exporting a filtered list from CRM and then importing the list into a free or paid mapping tool
3. Implement a mapping tool that extracts data from a CRM system through the CRM system’s API in order to automate the mapping process
4. Implement a mapping solution that both extracts data from CRM and returns data, such as geographic coordinates, back into the CRM system
Mapping Software Options Across These Four Levels
Let’s look at six of the mapping options that span these four levels. These are not all mutually exclusive.
1. View a Single Record Location Based on Address
Several CRM systems, by default, display a map on Lead, Contact, and Account records. These maps are a simple API call to Google Maps or Bing Maps based on address fields. The resulting map is embedded in the record.
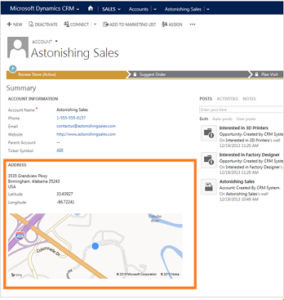
Out of the box, Microsoft Dynamics 365 provides a Bing map within each Lead, Account, or Contact record.
Salesforce has a Maps and Location setting which, when enabled, displays a Google Map under filled-in address fields in the Lead, Account, and Contact objects.
2. View a Single Record Location Based on IP Address
To maximize conversion rates, lead capture forms often do not request a visitor’s address information. However, it can be helpful to the salesperson who’s working a lead to visualize the Lead’s general location.
Most marketing automation systems capture a converted visitor’s IP address into a field in their system. A reverse IP lookup is then performed in order to populate the visitor’s city, region, and country into data fields. These fields can then be mapped into a CRM system via the marketing automation system’s integration.
The IP address fairly reliably indicates where the visitor was when they submitted the form. However, the IP address might not be an accurate reflection of their company’s headquarters location. The visitor may work remotely, or they may have been traveling when they visited the website.
3. Map a Filtered Set of Records for Free
Maps can also be created for filtered data sets, such as “Active Customers in Illinois”.
The simple and free way to map CRM data is to export a filtered list and then import it into Google My Maps. Google My Maps is included with both consumer Gmail and Google Workspace.
4. CRM Systems With Built-in Multi-Record Mapping
Pipedrive allows for viewing multiple customer locations on a map.
Nutshell allows users to filter their leads and customers by everything from source to industry, then view the results on an interactive map.
5. Standalone CRM Mapping Software (Some With Available CRM Integrations)
There are a number of paid mapping options that offer substantially more functionality than any of the free or included offerings.
Map My Customers
Map My Customers is a standalone mapping system that offers integrations with Zoho, Microsoft Dynamics 365 CRM, InfusionSoft, and Salesforce.
Badger
Badger is another standalone mapping tool. The home page message is, “The #1 Sales Route Planner in the App Store – 2016”.
Badger offers integration with Microsoft Dynamics 365.
Mapline
Mapline is a flexible mapping software that is primarily designed to integrate with Excel. Mapline does not appear to offer any CRM integrations.
eSpatial
eSpatial has announced a coming integration with Zoho.
6. Native Third-Party CRM Mapping Software
Several mapping software vendors have developed native mapping functionality within CRM applications.
Geopointe
Geopointe is a mapping solution designed specifically for Salesforce. Geopointe describes itself as “a native AppExchange application that location-enables Salesforce and brings actionable insights to our customers’ business processes.” Here is Geopointe’s explainer video:
Easy Territory
Easy Territory is a mapping solution for Microsoft Dynamics 365 CRM. While it runs natively within CRM, it can also run as a standalone application.
MapAnything
MapAnything is another Salesforce-specific solution.
MapAnything Express is a small business version of the product that’s built on the Salesforce platform — designed for companies that have not made a commitment to the full version of Salesforce.
There is certainly no shortage of available business mapping options. The right mapping software for a given organization depends on mapping requirements, including the level of integration with the CRM system that’s in place or is being considered.
For certain organizations evaluating a new CRM system, mapping requirements should be part of the overall requirements gathering process. Gathering requirements is our recommended first step of a seven-step process that should be followed in advance of selecting a new CRM system.



